The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is an autonomous body. It has the responsibility of regulating and developing the securities market in India. It is a regulatory body under the Ministry of Finance. Its head office is located at Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai.
Many students dreams of becoming a SEBI officer, where they can play a crucial role in the operations of trading and the stock exchange of India. Among all of this, there is one thing that left everyone buzzing over a major regulation that every SEBI employee is obliged to follow.
In this blog, we will understand the importance of SEBI as the securities market regulator. Moreover, we will also answer a very interesting question relating to the trading in securities by SEBI employees.
Before moving further, let’s have a brief introduction about what SEBI is all about and what is its importance.

What is SEBI?
SEBI was first established as a non-statutory body on April 12, 1988, through an Administrative Resolution of the Government of India with the objective of regulating and developing the securities market and protecting the interest of the investors. However, it was given statutory powers on January 30, 1992, with the passing of the SEBI Act 1992 by the Parliament. The SEBI Act came into force on April 04, 1992.
Why was SEBI Constituted?
SEBI was constituted because, before SEBI, the law relating to the regulation of securities was contained in different statutes. These are- the Companies Act, 1956, Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956, and the Capital Issues (Control) Act, 1947. This made regulation of the securities market difficult as the legislations were scattered and the administrative agencies did not have the proper expertise to deal with the investors.
However, the Government of India conferred additional statutory powers to SEBI in the year 1995 through an amendment to the SEBI Act, 1992.
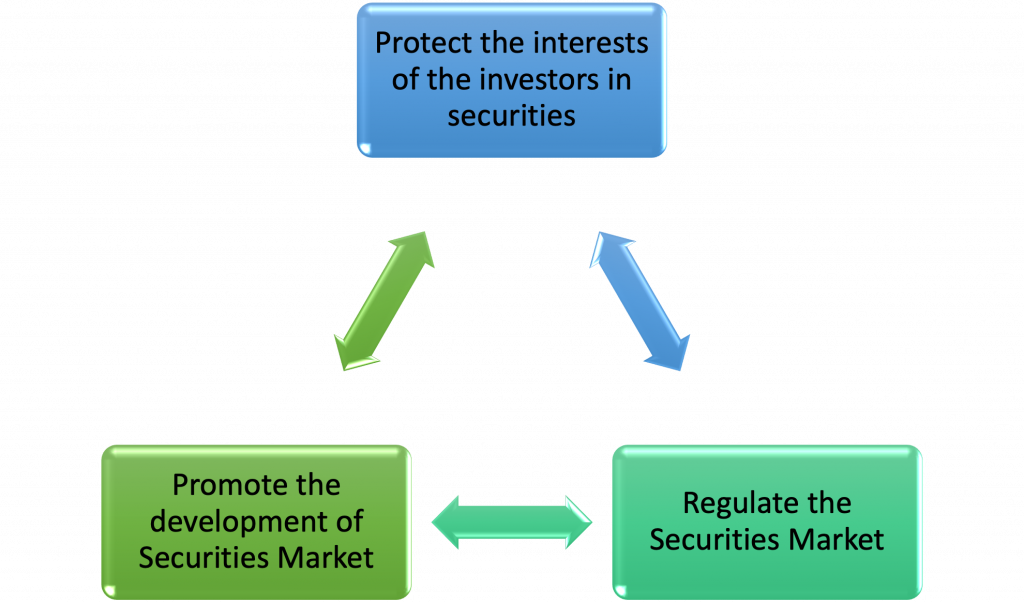
Objectives of SEBI
The preamble of the SEBI Act states the objective of the organization. They are as follows-
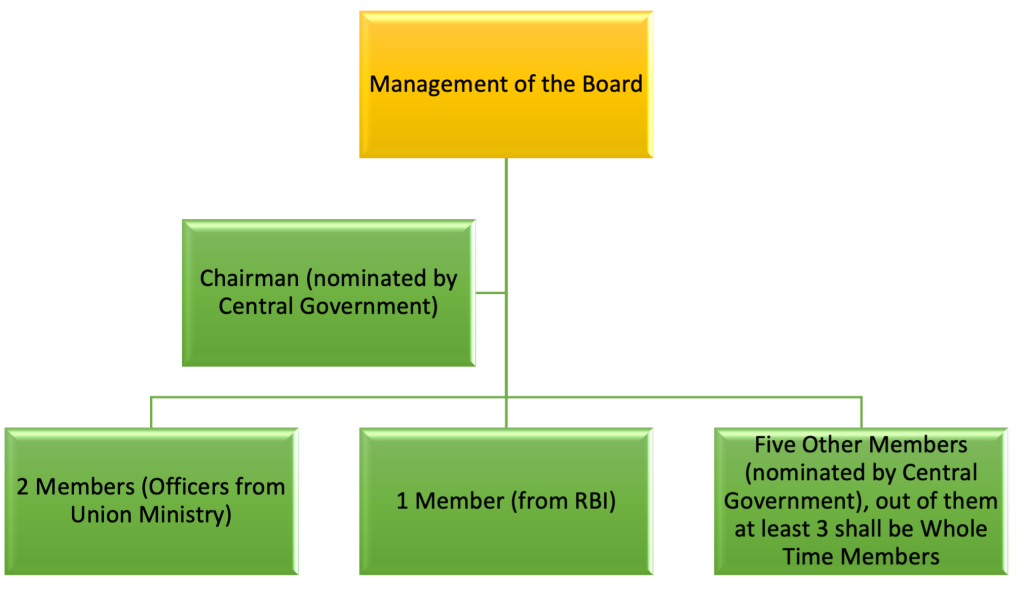
Structure of SEBI
The SEBI Board is managed by its members and consists of the following-
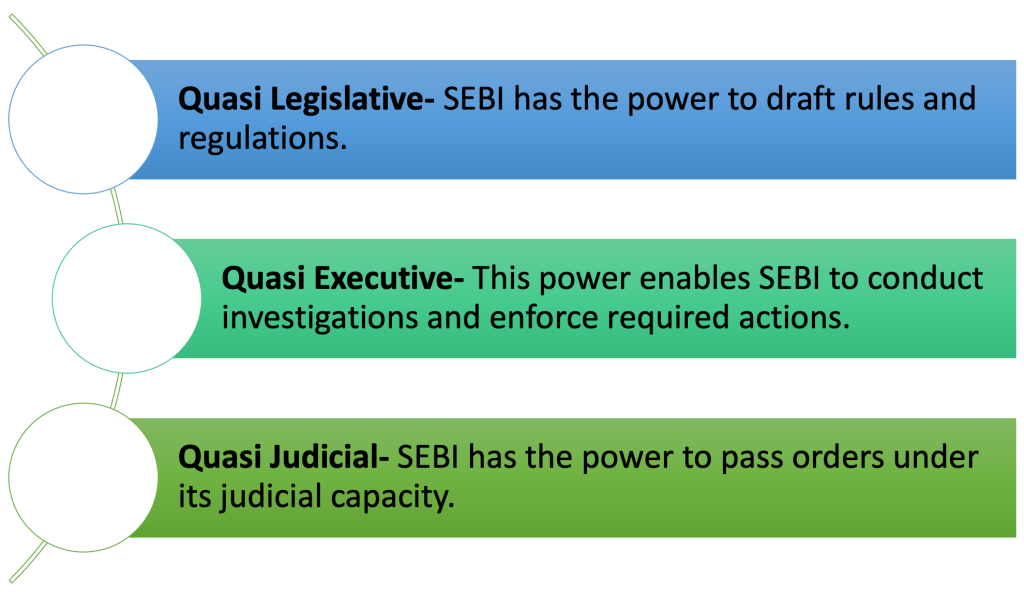
Powers of SEBI
SEBI is a very unique and powerful regulatory body because it has all three powers rolled into one single entity. These powers include-
Moreover, to ensure accountability, SEBI also provides an appeal process. An aggrieved party can file an appeal to the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT). SAT has the power of hearing and disposing the appeals against the orders passed by SEBI. Furthermore, a party aggrieved by the order of SAT can prefer a second appeal to the Supreme Court of India.
Functions of SEBI
Given below are some of the functions of SEBI-

Are SEBI Employees Allowed to Trade?
The securities market in India has developed manifold in the last few decades. Many people are now investing in the securities market because there is a potential of earning higher returns. During the Covid-19 pandemic, when so many people lost their jobs, the returns from the securities market offered a slight respite in the form of passive income. However, when it comes to its employees, SEBI has put several restrictions.
Now that we have understood what SEBI is and learned about its role, objectives, and powers, with respect to the securities market, let’s now look into another important aspect-
Can SEBI employees trade in the securities market?
The short answer is, No.
As per the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015, SEBI employees are prohibited from trading in securities.
SEBI issued the law of (Prohibition of Insider Trading Regulations) in 2015. Under this law, any professional acting as a KMP, board of directors, or associated with the promotor group in any way shall be prohibited from trading or investing in securities that are listed or happen to be listed in the Stock Exchange.
The law was last amended in November 2022 with the prohibition of communication of insiders about trading to any external body or person. The restriction of SEBI Employees from trading left people curious about the potential reasons behind it. You are going to know about those reasons later in this blog.
But before that, let us first understand the difference between Investment and Trading.
Investing
The purpose behind investing is to gradually build your wealth over an extended period of time. This is done through the buying and holding of a portfolio of stocks, mutual funds, bonds, and other investment instruments. Generally, investments are held for a period of years or even decades. This enables the investors to take advantage of benefits like interest and dividends along the way.
Trading
On the contrary, trading deals with more frequent transactions like- buying and selling of stocks, commodities and other instruments. The goal here is to make short-term gains by buying at lower prices and selling at higher prices. This is done within a relatively short period of time.
Let us look at the provisions in detail-
| Regulations | What They Provide |
| 63- Private Trading | It prohibits employees from engaging in any commercial business either on his own account or as an agent for others |
| 64- Restriction on Investments | No employee can make an investment either directly or indirectly in equity or equity related instruments including convertible debentures or warrants The employee will not invest- In his name or In the name of his dependent children or other wards managed by him as their guardian Investment made by spouse, dependent, children, dependent parents and parent-in-laws of the employee out of the money received from the employee. Exception- SEBI employees can invest in units of mutual funds, non- convertible debentures and bonds and in rights issues in respect of the shares already held by him. |
| 65- Speculation in Stock, Shares, Investments, etc. | (1) Employees are prohibited from engaging in ‘Badla’ trading/trade, speculating in stock, shares, securities or commodities of any description. (2) Employees having knowledge of unpublished price sensitive information shall not encourage any person to deal in securities to which it relates. (3) Each employee will be deemed as an “insider” within the meaning of Regulation 2 (1) (g) of the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations 2015 and the provisions of this regulation are applicable to each member of the Board. |
Reasons for not allowing SEBI Employees to Trade
Being a regulator of the securities market, it is the duty of SEBI to provide an equal footing to investors and traders. Given below are the reasons for not allowing SEBI employees to trade-
- SEBI employees play a special role in monitoring many sensitive activities of the stock market. Therefore, the employees are exposed to a lot of confidential information. This information may be used by an official to his/her advantage by using it ahead of time. So, allowing them to participate in the securities market will create a conflict of interest between the employees and the objectives of SEBI.
- Another important point to note is that, while regulating the stock market, SEBI employees also work very closely with various companies. Therefore, the employees fall under the purview of “insider” within the meaning of Regulation 2 (1) (g) of SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015. Hence, it would be unfair to allow the employees to invest in the securities market as they would possess knowledge of unpublished price-sensitive information.
- Maintaining an efficient market is the goal of a regulatory body. An efficient market is one, where current market prices accurately present all information available to the interested parties. In an efficient market, there would be no way of “beating” the market and making a profit from mispricings, as they would not exist. Therefore, it makes sense to keep SEBI officials away from participating directly in the securities market as market manipulation will not be possible.
The above mentioned restrictions will apply only when a person is already working with SEBI. However, the situation will be different before they join SEBI.
There are three questions that come to mind when we talk about the second situation. Let us understand in detail-
Q1) What happens if your parents/spouse/in-laws invest in the securities market before you become a part of SEBI? Do they have to withdraw from the market with immediate effect once you join SEBI?
- As per Regulation 66 of SEBI (Employees’ Service) Regulations, 2001, upon joining, every employee is required to declare a statement of all their assets and liabilities within 30 days as per Section 44 (2) of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013.
- Moreover, every employee has to file an annual return of such assets and liabilities with the Board before July 31 of every year as per Section 44 (4) of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013.
- Furthermore, if an employee enters into a transaction with respect to movable properties (including securities) either in his own name or in the name of a member of his family, he has to report such transaction to the competent authority within 30 days from the date of such transaction.
Q2) What happens if the person gets married/engaged before becoming a part of SEBI? Can their spouse/fiancé still invest in the securities market?
- The fiancé/spouse may invest in the securities market, but upon marriage when he/she becomes the spouse, then all rules will apply.
- Thus, the restrictions on investments under Regulation 65 of SEBI (Employees’ Service) Regulations, 2001 will apply to the spouse/fiancé of the employee in the same manner as the employee. As such, the spouse/fiancé will not be allowed to invest in the securities Market.
- However, these restrictions are there for trading and speculation purposes only. An employee and their spouse are allowed to invest in mutual funds for long-term savings and investment purposes.
Q3) If these violations aren’t taken care of, then what actions can SEBI take legally?
- If any employee violates any regulation, SEBI can impose penalties as per the nature of breach.
- Regulation 79 of the SEBI (Employees’ Service) Regulations, 2001 provides penalties for breach of regulations.
- The penalties are divided into minor and major penalties. Some of the minor penalties include- censure, withholding of promotion, withholding of increments of pay, etc. On the other hand, compulsory retirement, removal/termination of service, etc. are some of the major penalties.
- Moreover, Regulation 80 of the SEBI (Employees’ Service) Regulations, 2001 provides that major penalties can be imposed only after conducting an inquiry.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, we can conclude that SEBI plays an important role in protecting the interest of the investors and in the promotion & development of the securities market. For this purpose, SEBI has set up many checks and balances to promote a market that is both fair and efficient. The Prohibition of Insider Trading Act 2015, is the initiative to regularize and enhance the authenticity of SEBI and its fair functioning.
To know more about such interesting facts and information about India and its regulatory bodies. Stay updated with our daily blogs.
To help you prepare 50% faster for competitive exams, ixamBee provides free Mock Test Series and all the Current Affairs in English and Current Affairs in Hindi in the BeePedia capsules for GA Preparation. You can also get the latest updates for Bank PO, Bank Clerk, SSC, RBI Grade B, NABARD and Other Government Jobs.











