Question
The ratio of the compound
interest earned on an amount of Rs. 'p' at an interest rate of 15% per annum for 2 years to the simple interest earned on Rs. (p - 3000) at an interest rate of 12% per annum for 3 years is given as 129:90. Calculate the total interest obtained from both the compound interest and simple interest combined.Solution
ATQ, From the question: [p × (1 + 15/100) 2 – p]/[{(p – 3000) × 12 × 3}/100] = 129/90 [129p/400]/[{(p – 3000) × 36}/100] = 129/90 p/[4 × (p – 3000) × 2] = 1/5 5p = 8p – 24000 p = 8000 Now, CI received on Rs.8000 at a 15% rate after 2 years: 8000 × (1 + 15/100) 2 – 8000 = Rs.2580 And, SI received on Rs.5000 at a 12% rate after 3 years: (5000 × 12 × 3)/100 = Rs.1800 Required sum = 2580 + 1800 = Rs.4380
If, ( a + b = 14 ) and ( a² + b² = 106 ), then find the value of (a³ + b³).
If a + b + c + d = 4, then the value of
If, 6x + y = 20, and 2xy = 32, and 6x > y, then find the value of 216x³ – y³.
If x = 19 , find x 5 - 20 x 4 + 20 x 3 - 20x 2 + 20x - 20 = ?
If
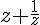 = -2 then find
= -2 then find The length of a rectangle is four times its breadth. If its length is increased by 20 cm and breadth is increased by 20 cm, the area of the rectangle is...
If n = 3 + √2, then find the value of (n + 1/n)².
If (x - 1) 3 + (y - 2) 3 + (z - 3) 3 + 3(x + y - 3)(y + z - 5)(x + z - 4) = 0, then what is the value of (x + y +...
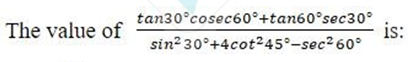
If √e + (1/√e) = 10, then find the value of e + (1/e).



