Question
Statements: Some bikes are cars. Some cars
are motors. No motor is cycle. Conclusions: I. Some cycle are definitely bikes. II. At least some motors are bikes. III. All cars being bikes is a possibility. IV. No bike is cycle. In each question below are given some statements followed by some conclusions numbered I, II, etc are given. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.Solution
Some bikes are cars(I) + Some cars are motors(I) ⇒ No conclusion. Hence conclusion I, II and IV does not follow but conclusion I and IV will form a complementary pair. Hence either conclusion I or IV follow. Some bikes are cars(I) ⇒ Conversion ⇒ Some cars are bikes(I) ⇒ Probable conclusion ⇒ All cars being bikes is a possibility.(A). Hence conclusion III follows. ALTERNATE SOLUTION: Minimal possibility: 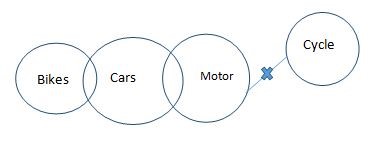
What is the theme of World Hindi Day in 2024?
Kanpur city was established in which of the following year?
The 12th Joint Working Group (JWG) on Border Management meeting is held on 15th and 16th June, 2022 between India and which other country?
What was the revised economic growth forecast for India in FY2024-25 as per the latest RBI’s MPC report?
Why does distilled water not conduct electricity?
Whose tomb is in Chunargarh, he is -
Lusaka is the capital of which of these countries?
Where was India's first Gati Shakti Research Chair established?
In the recent Brazilian F1 Grand Prix championship who became the winner of the year 2022?
Which queen died fighting Mughal armies while defending Garha Katanga in 1564?
Relevant for Exams:



