Question
Who among the following sits second to the left of
E? Study the following information carefully and answer the questions below: There are nine persons i.e. E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L and M are sitting in a triangular table such that three of them are sitting at the corner of the table and they are facing outside the table and two persons are sitting on each side of the table and they are facing inside the table. K and G are immediate neighbours of each other on the same side of the table. H sits third to the left of K. J sits two places away from H. E sits to the immediate right of J. Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbour of H.Solution
K and G are immediate neighbours of each other on the same side of the table. As per this statement, there are two possible cases and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 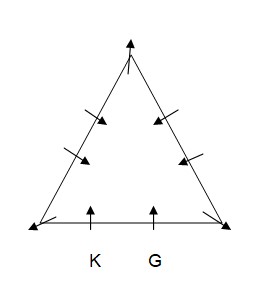 Case-2
Case-2 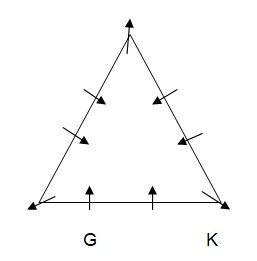 H sits third to the left of K. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
H sits third to the left of K. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 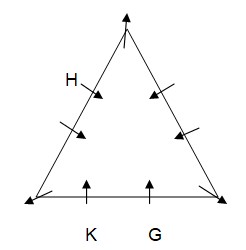 Case-2
Case-2 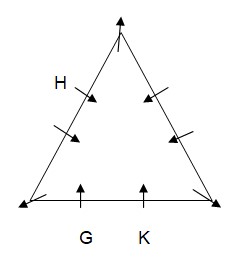 J sits two places away from H. As per this statement, CASE I will further get spilt into one more case and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
J sits two places away from H. As per this statement, CASE I will further get spilt into one more case and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 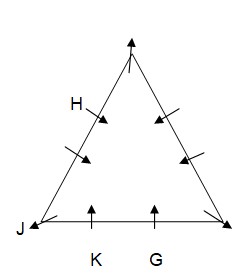 Case-1A
Case-1A 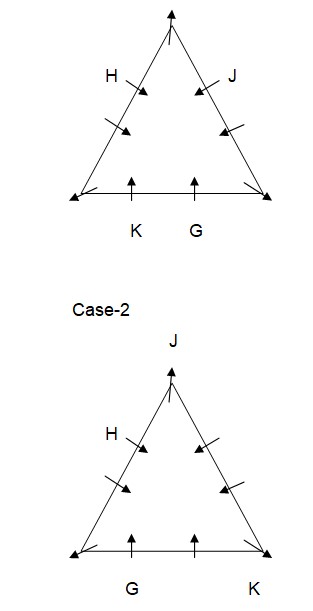 E sits to the immediate right of J. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this:
E sits to the immediate right of J. As per this statement, the arrangement will look like this: 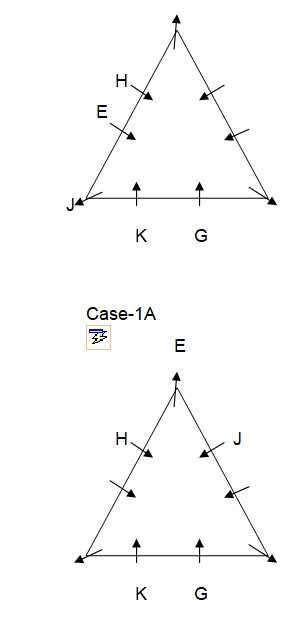 Case-2
Case-2 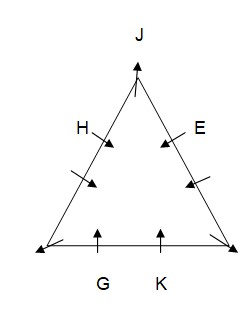 Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. As per this statement, CASE II will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I and CASE I (A) and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1
Only one person sits between G and F who is not an immediate neighbour of K. As per this statement, CASE II will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I and CASE I (A) and the arrangement will look like this: Case-1 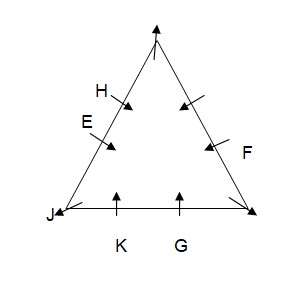 Case-1A
Case-1A 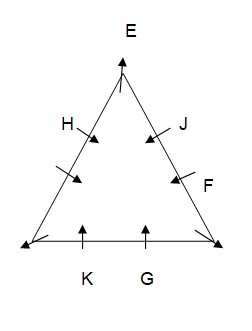 L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbor of H. As per this statement, CASE I will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I (A) and the final arrangement will look like this: Case-1A
L sits fourth to the right of I who is not an immediate neighbor of H. As per this statement, CASE I will get eliminated and we will continue with CASE I (A) and the final arrangement will look like this: Case-1A 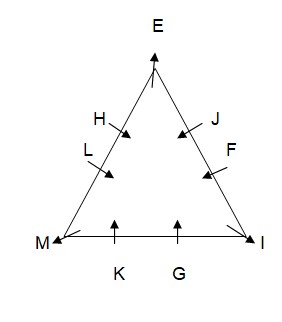
If a body of mass 5 kg is raised to 10 meters height, find its potential energy. (g = 9.8 m/s²)
A block of mass 2kg is pushed against a light spring of spring constant 200N/m and compressed by 0.2m on a horizontal surface with kinetic friction coe...
Find the power if a force of 100 N displaces an object by 10 m in 5 seconds.
Charges +q and –q are placed at (–d, 0) and (+d, 0). A third charge Q is placed at (0, x). For what value of x will the force on Q be maximum?
Ultra violet radiations of the Sun do not reach the earth because, earth's atmosphere is surrounded by –
What will happen to the volume of ozone, when it is heated?
Which of the following is an alpha particle which is emitted in radioactivity?
The polarization of electromagnetic waves demonstrates that they are:
The magnetic equator is closely associated with which of the following?
A capacitor filled with dielectric constant K is connected to a battery. If dielectric is removed, how much charge flows back?
Relevant for Exams:



