Question
What is the position of Q with respect to
W? Answer the questions based on the information given below. Ten persons P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y sit around a circular table such that four of them face outside while others face towards the centre. No two persons with names starting with consecutive alphabets are immediate neighbors of each other. T sits 4th to the left of Q, who faces outside. U sits immediate left of R, who faces towards the centre. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other. X sits 3rd to the left of R. S and T face same direction. Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P.Solution
T sits 4th to the left of Q, who faces outside. U sits immediate left of R, who faces towards the centre. X sits 3rd to the left of R. So, T sits either 2nd to the right of R or 4th to the left of R. Also, X sits either immediate right of Q or 5th to the left of Q. Case I: T sits 2nd to the right of R: 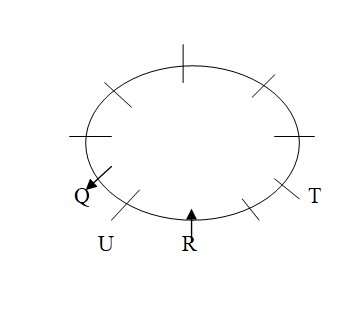 Case II: T sits 4th to the left of R:
Case II: T sits 4th to the left of R: 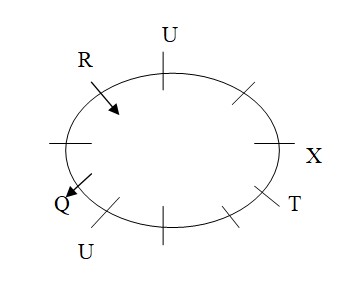 Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other, this is not possible in case II, so case II is rejected. S and T face same direction. So, S and T face towards the centre and V faces outside.
Two persons sit between X and P, who doesn’t sit 2nd to the left of T. S and V sits immediate left of each other, this is not possible in case II, so case II is rejected. S and T face same direction. So, S and T face towards the centre and V faces outside. 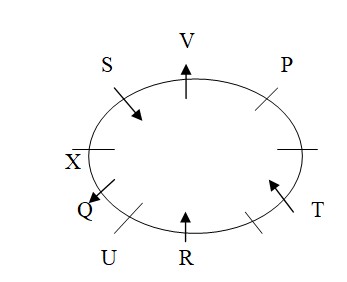 Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. So, W faces outside and sits adjacent to R and Y sits immediate right of T. Also, U and Y face towards the centre and P face outside. The final seating arrangement is given below:
Y doesn’t sit adjacent to R. V and W face same direction as P. U and Y face same direction as X. X doesn’t face outside. So, W faces outside and sits adjacent to R and Y sits immediate right of T. Also, U and Y face towards the centre and P face outside. The final seating arrangement is given below: 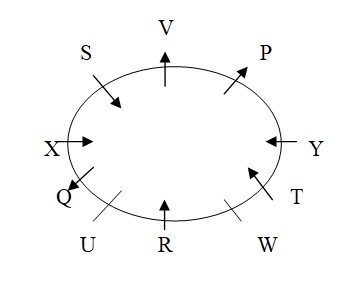
A right circular cone has a base radius of 4 cm and a height of 9 cm. If a cylindrical hole of radius 2 cm is drilled through the axis of the cone, what...
What is the principal sum if the difference between simple interest (SI) and compound interest (CI), compounded annually, on a ce...
A basket contains 4 yellow balls, 10 green balls, and 6 white balls. If two balls are taken out one after another without putting the first one back, fi...
A particular sum of money, when invested at a simple interest rate, yields Rs. 3,000 as interest after 2 years. The same sum, whe...
A class of 50 students has an average Chemistry exam score of 65. There average of boys and girls are 3: 2 in the class. Boys have an average score of 7...
Three boxes B1, B2, B3 contain red and green balls in the ratio 1:1, 3:5, and 5:3 respectively. A box is selected at random and a ball is drawn. What is...
What is the definition of an Internet Protocol (IP) address?
P can complete a work in 25 days, while Q can complete the same work in 30 days. They work together for 5 days, and then P is replaced by R, who can com...
Aman and Bhanu, working separately, can complete a task in 32 days and 40 days, respectively. They started working together, but ...
- What file extension does MS PowerPoint use by default?
Relevant for Exams:



