Question
What is the position of K with respect to the one whose
weight is 51kg, when counted anticlockwise? Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it. Twelve family members namely – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K and L sits in a hexagonal dining table in such a way that one person sits at each edge while one person sits at each corner. Person at the corner of the table sits facing center and person at the edge of the table sits facing away from center. Weight (Kg) of each person is different viz. 36, 39, 41, 42, 48, 51, 53, 64, 72, 84, 123 & 126. One person sits between E and B, whose weight is not 53kg but sits opposite to H. Weight of F is neither 48kg nor 64kg. The one whose weight is 48kg neither sits at edge nor is an immediate neighbor of C. Weight of L is twice the weight of H. The one whose weight is 123kg sits exactly opposite to the one whose weight is 53kg. Two persons sit between A and the one whose weight is 48kg. H neither sits adjacent to K nor his weight is 48kg. F sits exactly between J and the one whose weight is 72kg, who sits immediate left of G. One person sits between C and A, whose weight is 123kg. Weight of I is thrice the weight of H. C neither sits adjacent to B nor sits adjacent to E. The one whose age is 126kg and C sits together. Three persons sit between the one whose weight is 126kg and H. The one whose weight is 39kg not sits adjacent to K. Three persons sit between J and the one whose weight is 36kg. H sits adjacent to the one whose weight is 36kg. Difference between the weight of G and E is 12kg. One person sits between L and D. Three persons sit between the one whose weight is 51kg and the one whose weight is 64kg.Solution
We have: Two person sits between A and the one whose weight is 48kg. The one whose weight is 48kg neither sits at edge nor immediate neighbor of C, that means the one whose weight is 48kg sits at corner, thus in case (1) A sits third to right of the one whose weight is 48kg, in case (2) A sits third to left of the one whose weight is 48kg. One person sits between C and A, whose weight is 123kg. C neither sits adjacent to B nor sits adjacent to E, that means in case (1) C sits second to left of A, in case (2) C sits second to right of A. The one whose weight is 123kg sits exactly opposite to the one whose weight is 53kg. Based on above given information we have: Case-1 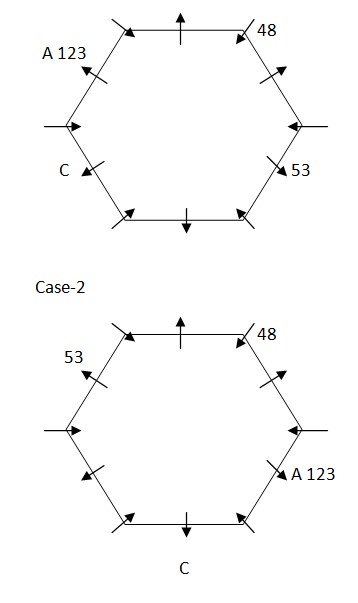 Again, we have: The one whose age is 126kg and C sits together, that means in case (1a) & case (2a) the one whose age is 126kg sits immediate right of C, in case (1b) & case (2b) the one whose age is 126kg sits immediate left of C. Three person sits between the one whose weight is 126kg and H. H neither sits adjacent to K nor his weight is 48kg. One person sits between E and B, whose weight is not 53kg but sits opposite to H, as E doesn’t sit adjacent to C, that means in case (1a) H sits third to left of C and weight of E is 48kg, in case (1b) H sits immediate right of A and E sits fifth to left of C, in case (1c) H sits fifth to left of C and E sits immediate right of A, in case (2a) H sits fifth to right of C and E sits immediate left of A, in case (2b) H sits third to right of C and weight of E is 48kg, in case (2c) H sits immediate left of A and E sits fifth to right of C. Based on above given information we have:
Again, we have: The one whose age is 126kg and C sits together, that means in case (1a) & case (2a) the one whose age is 126kg sits immediate right of C, in case (1b) & case (2b) the one whose age is 126kg sits immediate left of C. Three person sits between the one whose weight is 126kg and H. H neither sits adjacent to K nor his weight is 48kg. One person sits between E and B, whose weight is not 53kg but sits opposite to H, as E doesn’t sit adjacent to C, that means in case (1a) H sits third to left of C and weight of E is 48kg, in case (1b) H sits immediate right of A and E sits fifth to left of C, in case (1c) H sits fifth to left of C and E sits immediate right of A, in case (2a) H sits fifth to right of C and E sits immediate left of A, in case (2b) H sits third to right of C and weight of E is 48kg, in case (2c) H sits immediate left of A and E sits fifth to right of C. Based on above given information we have: 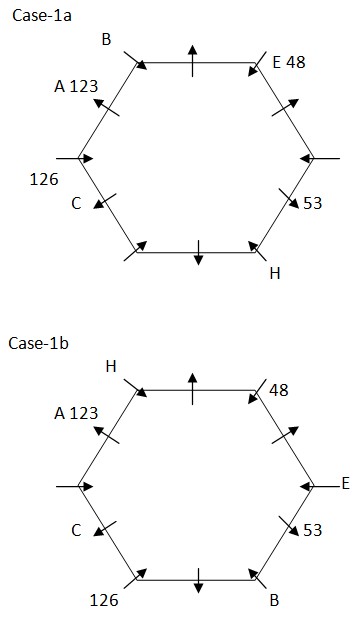
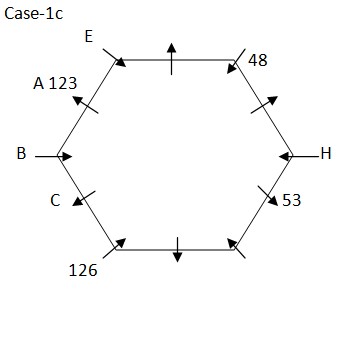 Case-2a
Case-2a 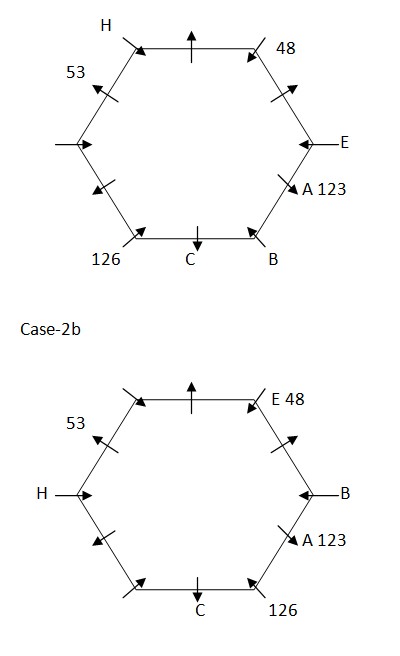 Case-2c
Case-2c 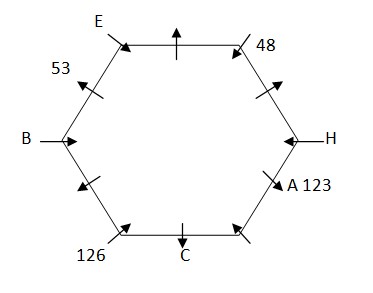 Again, we have: F sits exactly between J and the one whose weight is 72kg, who sits immediate left of G. Weight of F is neither 48kg nor 64kg. Three person sits between J and the one whose weight is 36kg. H sits adjacent to the one whose weight is 36kg, that means in case (1a) weight of F is 126kg and weight of G is 36kg, in case (2c) F sits second to left of J and G sits immediate right of A and case (1b), case (1c), case (2a) and case (2b) are not valid . Based on above given information we have:
Again, we have: F sits exactly between J and the one whose weight is 72kg, who sits immediate left of G. Weight of F is neither 48kg nor 64kg. Three person sits between J and the one whose weight is 36kg. H sits adjacent to the one whose weight is 36kg, that means in case (1a) weight of F is 126kg and weight of G is 36kg, in case (2c) F sits second to left of J and G sits immediate right of A and case (1b), case (1c), case (2a) and case (2b) are not valid . Based on above given information we have: 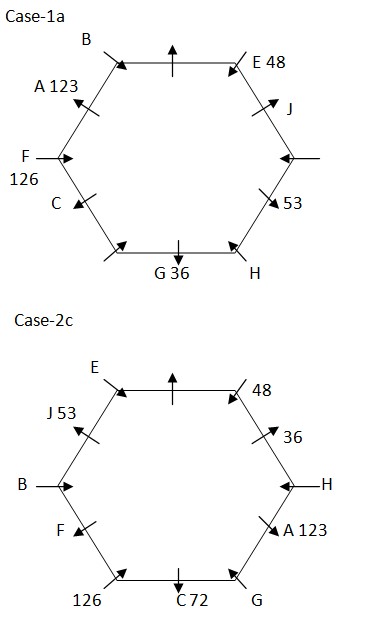 Case (1b), case (1c), case (2a) & case (2b) are not valid as F sits exactly between J and the one whose weight is 72kg, who sits immediate left of G . Again, we have: Weight of I is thrice the weight of H, since only such possible combination are (41, 123) & (42, 126), thus weight of H must be 42kg and that of I must be 126kg. Since, weight of I is 126 Weight of L is twice the weight of H, thus weight of L is 84kg. One person sits between L and D, that means L sits immediate left of E. Difference between weight of G and E is 12kg. The one whose weight is 39kg not sits adjacent to K, that means weight of weight of G must be 51kg and weight of E is 39kg. Three person sits between the one whose weight is 51kg and the one whose weight is 64kg, thus weight of B must be 64kg. As, remaining person is F, thus weight of F must be 41kg. Case (1a) is not valid as weight of I is 126kg. Based on above given information we have final arrangement as follow: Case-2c
Case (1b), case (1c), case (2a) & case (2b) are not valid as F sits exactly between J and the one whose weight is 72kg, who sits immediate left of G . Again, we have: Weight of I is thrice the weight of H, since only such possible combination are (41, 123) & (42, 126), thus weight of H must be 42kg and that of I must be 126kg. Since, weight of I is 126 Weight of L is twice the weight of H, thus weight of L is 84kg. One person sits between L and D, that means L sits immediate left of E. Difference between weight of G and E is 12kg. The one whose weight is 39kg not sits adjacent to K, that means weight of weight of G must be 51kg and weight of E is 39kg. Three person sits between the one whose weight is 51kg and the one whose weight is 64kg, thus weight of B must be 64kg. As, remaining person is F, thus weight of F must be 41kg. Case (1a) is not valid as weight of I is 126kg. Based on above given information we have final arrangement as follow: Case-2c 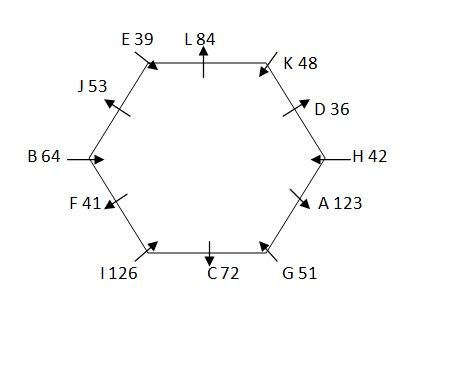
With reference to the revolutionary activism in India, consider the following statements:
1. It was a violent movement based on mass activity.
- What does an increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) signify?
Statements:
(I) A rise in retail prices
(II) An increase in consumers... The United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution in December, ___ declaring March 22 as World Water Day.
- During which 1929 session was the aim of 'Poorna Swaraj' (complete independence) adopted by the Indian National Congress?
Who has been appointed as the country director of Asian Development Bank (ADB) for India?
How many gold medals did India win at the 18th Asian Games in Jakarta and Palembang, Indonesia?
Which of the following was NOT a common goal of India's Five-Year Plans?
- In which environment do mangroves primarily flourish?
Why does seawater appear blue?
- John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton were awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics for which of the following achievements?
Relevant for Exams:



