Question
What is the position of the box with lily?
Answer the questions based on the information given below. Seven boxes viz. A, B, C, D, E, F and G are filled with different flowers viz. Rose, Lily, Jasmine, Orchid, Daisy, Tulip and Marigold are kept one above another in a stack. The box kept at the lowermost position is numbered as 1 and the box kept at the topmost position is numbered as 7. Box F is kept four boxes above the box with tulip where the box with daisy is kept exactly in the middle between them. Only two boxes are kept between the box with daisy and box E which is not kept at the topmost position. As many boxes kept above box E as below the box with Marigold which is kept two boxes away from box D. Box G with orchid is kept at an odd numbered position. Box C is kept immediately above the box with lily and two boxes below box B. The box with rose is kept immediately below the box with jasmine.Solution
Box F is kept four boxes above the box with tulip where the box with daisy is kept exactly in the middle between them. Only two boxes are kept between the box with daisy and box E which is not kept at the topmost position. 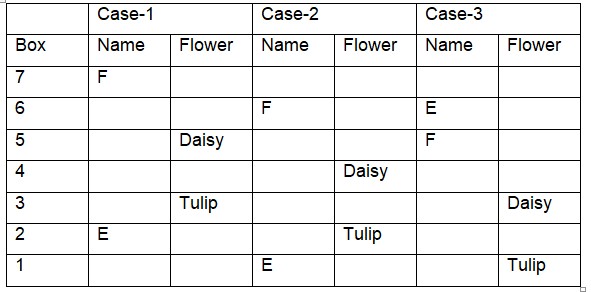 As many boxes kept above box E as below the box with Marigold which is kept two boxes away from box D. Box G with orchid is kept at an odd numbered position.
As many boxes kept above box E as below the box with Marigold which is kept two boxes away from box D. Box G with orchid is kept at an odd numbered position. 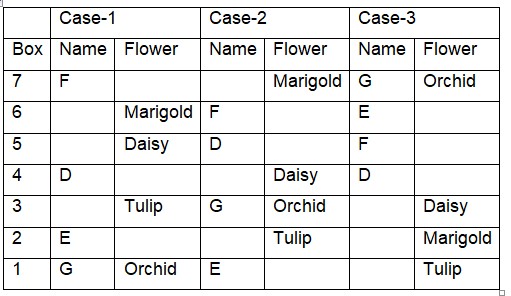 Box C is kept immediately above the box with lily and two boxes below box B. The box with rose is kept immediately below the box with jasmine. Hence, cases 1 and 3 get eliminated
Box C is kept immediately above the box with lily and two boxes below box B. The box with rose is kept immediately below the box with jasmine. Hence, cases 1 and 3 get eliminated 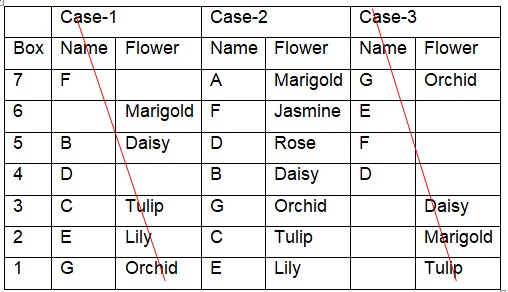 So final arrangement-
So final arrangement- 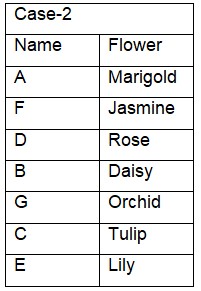
मन्त्र नामक सॉफ्टवेयर किसके द्वारा विकसित किया गया ?
स्मृति आधारित कौन से अनुवाद टूल को प्राइज के अंतर्गत बताय�...
नीचे दी गई तालिका में वाक्यों के सही अनुवाद का मिलान करें �...
लीला अंग्रेजी के अतिरिक्त भारतीय भाषाओं में उपलब्ध है ?
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से ‘विधिसम्मत’ का सही पर्याय है ?
...निम्नलिखित प्रश्न में एक अंग्रेजी का शब्द दिया गया है। उस...
दिए गए वाक्य का उचित हिंदी अनुवाद चुने –
The notification shall come into fo...
Assets का सही हिंदी अर्थ क्या है ?
नीचे दिए गए शब्दों का सही अनुवाद विकल्पों से चयन करें:
�...
निम्नलिखित प्रत्येक प्रश्न को चार भागों में बांटा गया है�...
Relevant for Exams:



