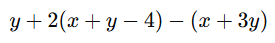Question
Which of the following is the most important reason for
calculating the sample size correctly in data analysis?Solution
Calculating the correct sample size is crucial because it directly impacts the reliability and validity of the analysis. A sample that is too small may not accurately represent the population, leading to underrepresentation of key subgroups and insufficient statistical power to detect significant differences or trends. A properly sized sample ensures that the results are reliable and that the findings can be generalized to the population. Statistical power is essential to determine the likelihood that a true effect will be observed, reducing the risk of Type II errors (failing to detect a true effect when one exists). The other options are incorrect because: • Option 1 (Including every possible outcome) is unrealistic and unnecessary in sampling, as sampling involves working with a subset, not the whole population. • Option 3 (Simplification) overlooks the importance of ensuring that the sample is large enough to draw valid conclusions. • Option 4 (Bias toward a segment) is undesirable, as sample size calculation aims to avoid bias and ensure representativeness. • Option 5 (Data cleaning) relates to dataset preparation but is not directly influenced by the sample size calculation itself.