Question
Statements: Some banks are lockers.
Some lockers are stores. Some stores are panels. Conclusions: I. No bank is a store. II. Some stores are banks. III. Some lockers are not panels. In each question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the two given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.Solution
Some banks are lockers(I) + Some lockers are stores(I) ⇒ No conclusion. Hence, conclusion I and II will not follow but they will form a complementary pair. I + I = No conclusion. Hence, conclusion III will not follow. Alternate Method: Relevant Possible cases: 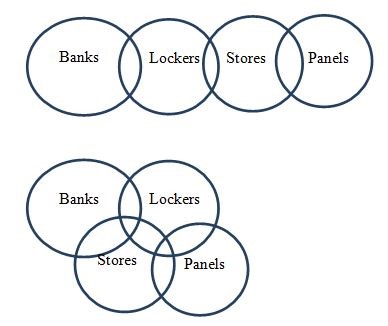
As per loan review framework of RBI, loan review of low value accounts are usually carried out __________
On what basis is an individual resident Indians permitted to include NRI close relatives as a joint holder in resident bank account?
Persons other than individuals can remit funds overseas, towards donations for certain specified purposes, up-to ____
The Reverse Repo Rate is used by RBI to:
JAM Trinity has played a significant role in the process of inclusive development in our country. Which of the following correctly describes JAM Trinity?
Which of the following statements regarding the classification of financial markets is/are correct?
1. Debt markets are primarily concerned with ...
What is the concessional rate of interest provided under the Differential Rate of Interest (DRI) Scheme?
The bonds prices _____ with increase in interest rates.
Which of the following is not correct with regard to oligopoly?
A manager adhering to the principles of "Level 5 Leadership," as defined by Jim Collins, would be characterized by a unique blend of personal humility a...



