Question
If all the persons are arranged in alphabetical order
in the clockwise direction with respect to A, then how many persons remain unchanged in their position (Excluding A)? Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions Eight persons – A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting in the square table such that all of them are facing towards the center. Four persons are sitting in the middle of the sides of the table and four persons are sitting at the corner of the table. All the information is not necessarily in the same order. A sits second to the left of G, who sits at one of the corner of the table. H sits either to the immediate right or to the immediate left of A. D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A. E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F.Solution
A sits second to the left of G, who sits at one of the corner of the table. H sits either to the immediate right or to the immediate left of A. From the above condition, there are two possibilities. 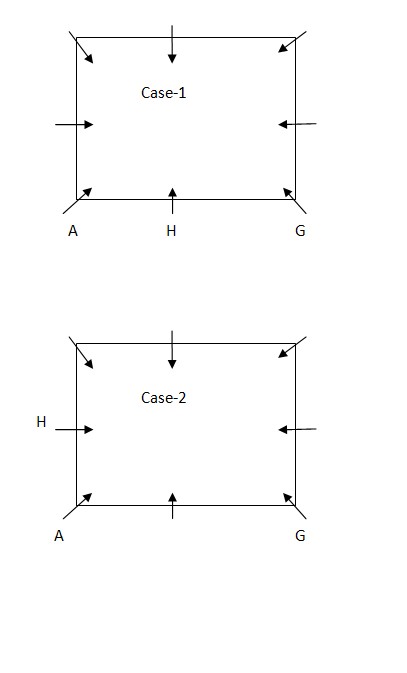 D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A
D sits opposite to the one who sits second to the left of C. C sits in the middle of the sides of table. D is neither the immediate neighbor of G nor A 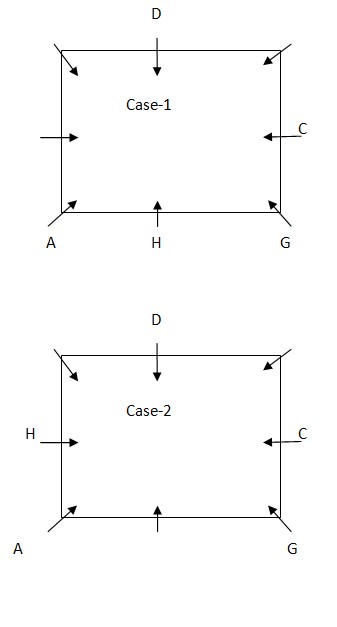 E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F. From the above condition, case1 gets eliminated. Case 2 shows the final arrangement.
E is the immediate neighbor of either of A or F, but not the both. B sits second to the left of F. From the above condition, case1 gets eliminated. Case 2 shows the final arrangement. 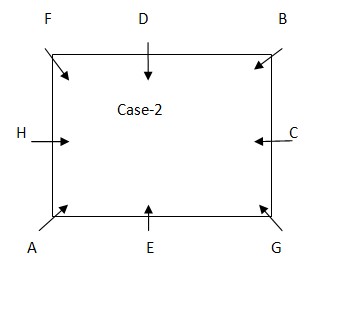
What is the primary objective of the MoU signed between the Technology Development Board (TDB) and the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)?
Who is the chairman of the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)?
Which Indian state celebrates the Karaga festival annually?
How many athletes from the eight North Eastern states participated in the 3rd edition of the North East Games 2024 held in Nagaland?
The Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) system enhances which aspect of naval warfare?
For which poetic work was renowned poet Prabha Varma selected for the Saraswati Samman for the year 2023?
Consider the following statements about Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award:
1. Recently Chirag Shetty and Rankireddy Satwik Sai Raj won the Maj...
What is the total prize money for the Hockey India League (HIL) 2024-25 edition?
Who is the current Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi?
What percentage reduction was recorded in India’s Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) under NHM?
Relevant for Exams:



