Question
The ratio of the monthly incomes of A and B is 11: 13
and the ratio of their expenditures is 9: 11. If both of them manage to save ₹4,000 per month, then find the difference in their incomes (in ₹).Solution
Let, the monthly income of A = 11x The monthly income of B = 13x The monthly expenditures of A = 9y The monthly expenditures of B = 11y So, 11x - 9y = 4000 .....(1) 13x - 11y = 4000 .....(2) (1) × 11 - (2) × 9 gives, 121x - 99y - 117x + 99y = 44000 - 36000 ⇒ 4x = 8000 ⇒ x = 8000/4 = 2000 ∴ A's income = 11 × 2000 = Rs. 22000 ∴ B's income = 13 × 2000 = Rs. 26000 The difference of income = 26000 - 22000 = Rs. 4000 Alternate method 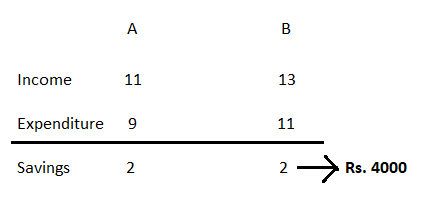 The difference = 2 ratio = Rs. 4000 Their income difference = 13 - 11 = 2 ratio ∴ Income difference = Rs. 4000 ∴ The difference between A and B's incomes (in Rs.) is Rs. 4000
The difference = 2 ratio = Rs. 4000 Their income difference = 13 - 11 = 2 ratio ∴ Income difference = Rs. 4000 ∴ The difference between A and B's incomes (in Rs.) is Rs. 4000
The length of the each side of an equilateral triangle is 42√3. The area of incircle, (cm 2 ) is
The perimeter of a rectangle is 60 meters. If the length of the rectangle is twice the width, find the area of the rectangle.
If median AD of an equilateral ∆ABC is 21 cm and G is centroid. Find GD?
The internal bisector of ∆ABC at ∠A cuts BC on D and cuts the circum circle at E if DE = 6cm, AC = 8cm and AD = 10 cm then find the length of AB?
- A tangent is drawn from an external point P to a circle, touching the circle at point Q such that PQ = 16cm. A secant PRS is also drawn from P, intersectin...
In the given figure, B and C are the centres of the two circles. ADE is the common tangent to the two circles. If the ratio of the radius of both the ci...
The lengths of three medians in a triangles are 21 cm, 28 cm, 35 cm. What is the area of that traingle (in cm 2 )?
in the given figure, ABCD is a square whose side is 4 cm. P is a point on the side AD. What is the minimum value (in cm) of BP + CP ?
If in a ΔABC, the external angle bisector of angle A, meets BC when extended at a point D, BD = 5cm , BC = 3 cm then what is AB:AC ?
If G is the centroid and AD, BE, CF are three medians of ∆ABC with area 72 cm 2 , then the area of ∆BDG is?
Relevant for Exams:



