Question
Statements: No cow is a bull.
No bull is a goat. Some goat are sheep. Conclusions: I. Some bull being goat is a possibility. II. Some goat are not cow. III. Some sheep are goat. In each question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the two given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the three given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.Solution
No bull is a goat (E) ⇒ No conclusion. Hence, conclusion I will not follow. No cow is a bull (E) + No bull is a goat (E) ⇒ No conclusion. Hence, conclusion II will not follow. Some goat are sheep(I) ⇒ Conversion ⇒ Some sheep are goat(I). Hence, conclusion III follows.
26% of 950 + 50/3% of 7962 = ?
- What will come in place of (?) in the given expression.
(84 + 36 ÷ 6) × 2 = ? 690 ÷ (75% of 460) = ? ÷ (50% of 160)

21% of 400 − 150 = ? − 77
Evaluate: 320 − {18 + 4 × (21 − 9)}
What will come in the place of question mark (?) in the given expression?
(50 × 6 ÷ 12) × 9 = ?
(24% of 500 - 20) ÷ 25 = ? ÷ 4
√ (12+√ (12+√ (12+ ⋯ ∞ ))
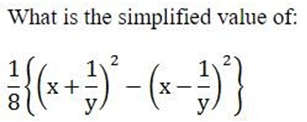
Relevant for Exams:



