Question
D, E, F, G, J, K, L are sitting around a circular table
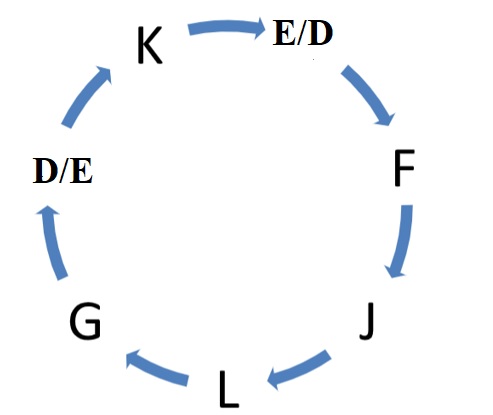
facing the centre, but not necessarily in the same order. J is the immediate neighbor of L and F. G is neither an immediate neighbor of F nor E. K, who is sitting second to the left of G has D and E are immediate neighbors. Who is sitting to the immediate right of G?Solution
Which Indian town, established by Rabindranath Tagore and known as the "abode of peace," has been included in UNESCO's World Heritage List?
“Maitri Diwas or Friendship Day” is celebrated on which day to mark the day on which India recognised newly-formed Bangladesh in 1971.
Alipay Singapore Holding is going to sell its entire 3.44 per cent stake in Zomato which will help raise__________ .
What is the primary purpose of Qualified Institutional Placement (QIP) for listed companies?
How many individuals were identified as extremely poor under Kerala’s Extreme Poverty Eradication Programme?
Match the following nuclear power stations with their correct locations:
(I) Narora Atomic Power Station (1) G...
Identify the correct pair for SIDBI’s founding date and headquarters.
What is the title of the book authored by Srinath Raghavan, chronicling Indira Gandhi’s political years?
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) has cancelled the “Khadi Certification” of its oldest Khadi Institution named ...
Government compiles estimates of rural and urban income, in terms of Per Capita Net Value Added (NVA), only in the base year of the Gross Domestic Produ...
Relevant for Exams:



