Question
Who is the husband of V?
Answer the questions based on the information given below : P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are sitting around a circle facing the centre but not necessarily in the same order. Each of them has a relationship with P. V is sitting second to the left of father of P. U is immediate neighbor of P. S, mother of P is sitting opposite to the sister of P. Q is sitting to the immediate right of wife of P. T is sitting to the immediate left of sister of P. T who is a male is sitting second to the right of mother of R. Brother of P is sitting third to right of Q. Daughter of P is sitting to third to right of sister of P. P is sitting second to the right of daughter of T. V has two children in different genders.Solution
S, mother of P is sitting opposite to the sister of P. 2. Daughter of P is sitting to third to right of sister of P. 3. T is sitting to the immediate left of sister of P. 4. Q is sitting to the immediate right of wife of P. Brother of P is sitting third to right of Q. Case-1 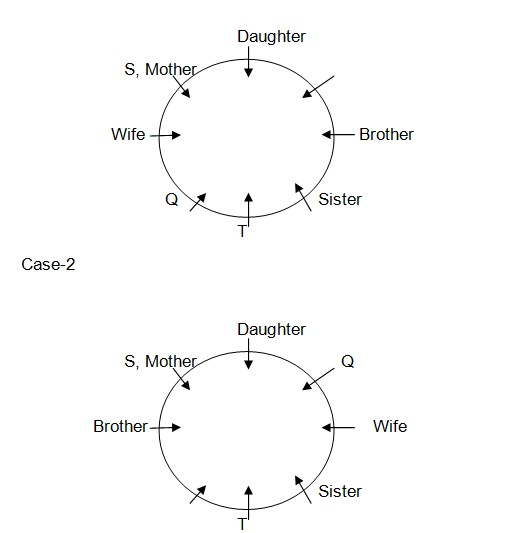
 Next we have only 1 position left for placing P in all 3 arrangements as Case-1
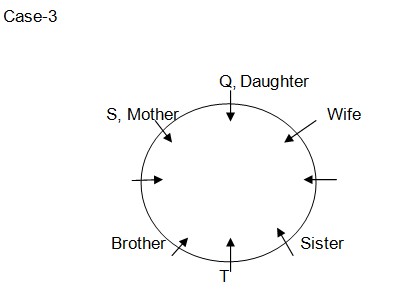
Next we have only 1 position left for placing P in all 3 arrangements as Case-1 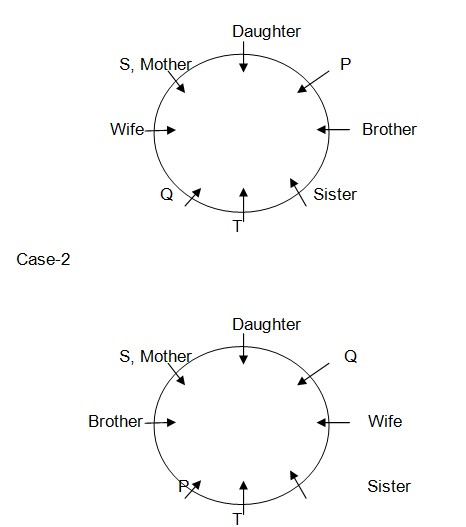
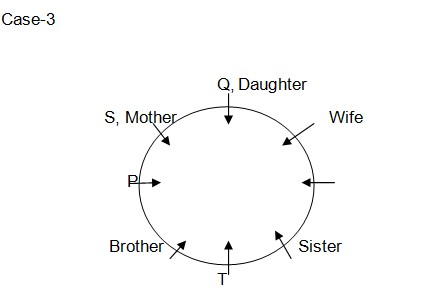 P is sitting second to the right of daughter of T. T who is a male is sitting second to the right of mother of R. V is sitting second to the left of father of P. U is immediate neighbor of P. V has two children in different genders. So final arrangement Case-2 & 3 gets rejected as these both cases were not satisfied with 8th statement (as we know P is a male member) In case-1, P’s sister, P’s brother and P’s daughter were seated apart from Q. This implies Q must be son of P and the blood relation is shown below,
P is sitting second to the right of daughter of T. T who is a male is sitting second to the right of mother of R. V is sitting second to the left of father of P. U is immediate neighbor of P. V has two children in different genders. So final arrangement Case-2 & 3 gets rejected as these both cases were not satisfied with 8th statement (as we know P is a male member) In case-1, P’s sister, P’s brother and P’s daughter were seated apart from Q. This implies Q must be son of P and the blood relation is shown below, 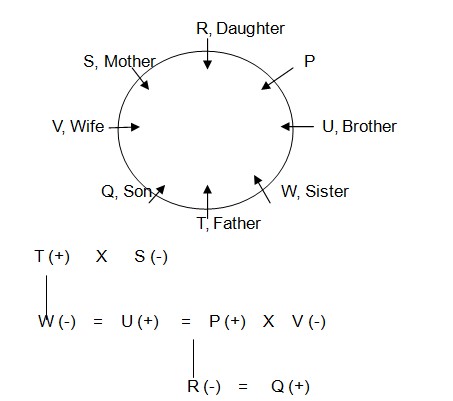
Which country tops the list of the most liberal countries in the world for 2024, showcasing dominance in progressive social policies, gender equality, a...
What is the current number of tax slabs under the GST regime in India?
Which Indian company announced the development of 'JioBrain,' a comprehensive suite of AI tools?
Who was the winner of the Miami Grand Prix 2022?
The President of Mongolia, Ukhnaagiin Khurelsukh gifted a _______ to the Rajnath Singh, the first Indian Defence Minister as a token of gratitude.
Recently the Chief Minister of West Bengal, Smt Mamta Banerjee has announced how many new districts in the state to make the total of 30 districts.
In which year did the Battle of Plassey take place?
The USA led ‘Chip 4’ is a strategic alliance of four countries, one is USA, Japan, Taiwan and _____
What is the primary aim of the 'IndusInd Bank Samman RuPay Credit Card' launched by IndusInd Bank?
It's Girls4Tech programme in India is related to
Relevant for Exams:



