Question
How many persons sit between V and R when counted from
the right of R? Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions Eight persons- Q, R, S, T, U, V, W and X are sitting around the square table facing the centre. Four of them sit in the corner and four of them sit in the middle of the sides of the table, but not necessarily in the same order. T sits third to the left of U. One person sits between U and Q who sits at the corner of the table. S and X sit opposite to each other. S is not an immediate neighbour of Q.R sits second to the left of S.W sits second to the right of V.Solution
T sits third to the left of U. One person sits between U and Q who sits at the corner of the table. From the above condition, there are two possibilities. 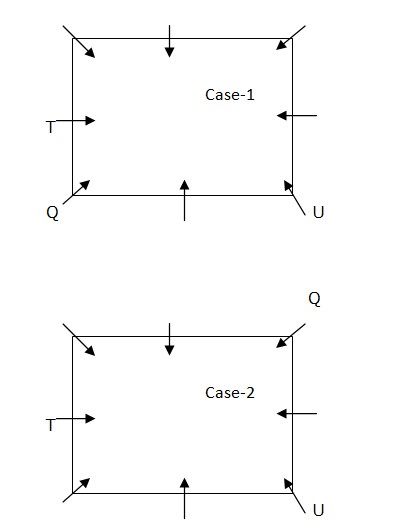 S and X sit opposite to each other. S is not an immediate neighbour of Q. R sits second to the left of S. From the above condition, case2 gets eliminated.
S and X sit opposite to each other. S is not an immediate neighbour of Q. R sits second to the left of S. From the above condition, case2 gets eliminated. 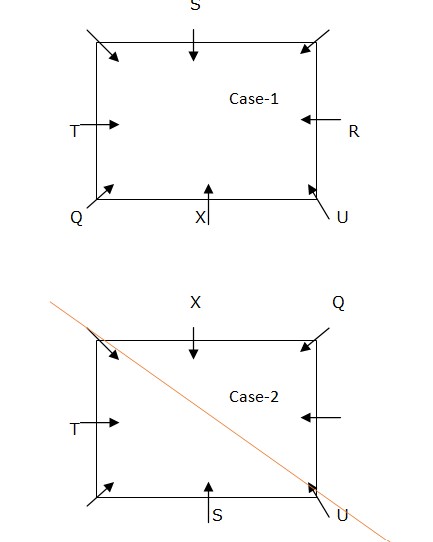 Again we have, W sits second to the right of V. From the above condition, case1 shows the final arrangement.
Again we have, W sits second to the right of V. From the above condition, case1 shows the final arrangement. 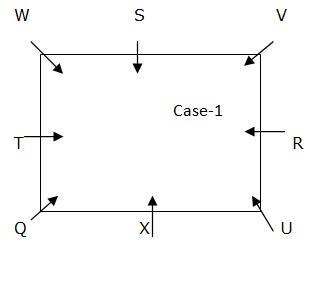
Araku Valley is located in which of the following state?
Chungthang town is situated in which Indian States?
In case of interstate transactions, the centre would levy & collect the integrated goods and services tax (IGST) under article 269A (I) of the constitu...
अफीम के पौधे का कौनसा हिस्सा औषधीय महत्व का है ?
Garo, Khasi, Jaintiya hills are located in which hills ?
Human Development index was formulated by which of the following organization?
Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary is located in which state?
The Book ‘ A voice of Freedom ’ is written by
In the parliamentary dignitaries is included:
1. Speaker of Lok Sabha
2. Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha
3. General Secretary of Lok Sa...
Which virus strain has raised concerns for potentially being transmitted from pigs to humans?
Relevant for Exams:



