Question
Who sits second right of
I? Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below it. Ten people A, B, C, D,E, F, G, H, I and J are sitting in two rows. Five people in each row facing each other. A, B, C, D and E are facing north. F, G, H, I and J are facing south but not necessarily in the same order. One who is sitting opposite to C sits immediate left of H. C sits third to the right of A. Only one person sitting between H and J. J is sitting one of the right positions of H. One who is sitting opposite to G sits third to the left of B. But B is not sitting at the extreme ends. Number of persons sitting to the left of F and number of persons sitting to the Left of E is same. Only two people are sitting between J and I.Solution
C sits third to the right of A. One who is sitting opposite to C sits immediate left of H Case-1 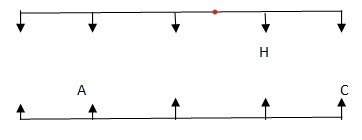 Case-2
Case-2 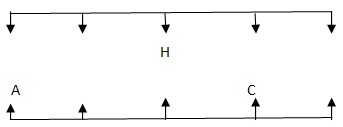 Only one person sitting between H and J. J is sitting one of the right positions of H. Only two people are sitting between J and I. Case-1
Only one person sitting between H and J. J is sitting one of the right positions of H. Only two people are sitting between J and I. Case-1 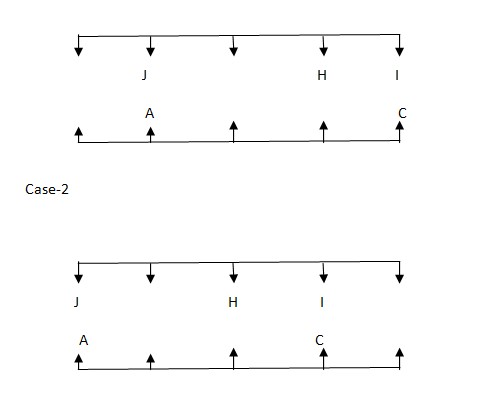 One who is sitting opposite to G sits third to the left of B. Case-1
One who is sitting opposite to G sits third to the left of B. Case-1 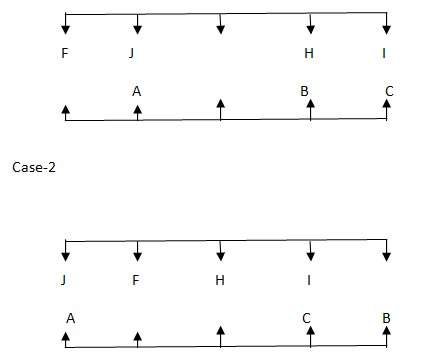 But B is not sitting at the extreme ends. Since Case (2) is not possible. Case-1
But B is not sitting at the extreme ends. Since Case (2) is not possible. Case-1 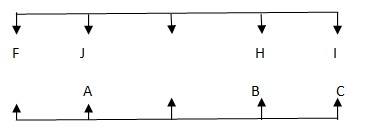 Number of persons sitting to the left of F and number of persons sitting to the Left of E is same. So the final arrangement is Case-1
Number of persons sitting to the left of F and number of persons sitting to the Left of E is same. So the final arrangement is Case-1 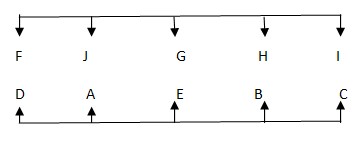
In the question below there are three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the three given statements to be true even if t...
Statements:
Every pilot is doctor.
34% doctors are teachers.
Few teachers are lawyers.
Conclusions:
I. Some pilots ar...
Statements:
Only a few Comedians are Hosts.
All Hosts are Anchors.
No Anchor is a Show.
Conclusions:
I. Some Comedi...
Statements:
Some Lantern are Light.
Only a few Light are Lamp.
Some Lamp are Torch.
Conclusions:
I. Some T...
Read the given statements and conclusions carefully. Assuming that the information given in the statements is true, even if it appears to be at variance...
In the questions given below, there are three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the three given statements to be true e...
In the question below there are three statements followed by three conclusions I, II and III. You have to take the three given statements to be true ev...
- In the question below some statements are given followed by three conclusions I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they ...
In the questions given below, there are three statements followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the three given statements to be true ...
In the question below are given some statements followed by some conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be ...
Relevant for Exams:



