Question
Among E, G, H, I, J and K, who is second to the left of
G if all are sitting around a circular table facing the centre. I. J sits third to left of G, who is not an immediate neighbour of K. H is second to the left of K. II. I sits opposite to J and is the immediate neighbour of K and E. H is sitting immediate right of E. Each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II are given below. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and –Solution
From I, 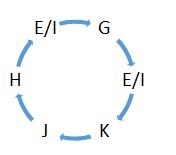 K is sitting second to the left of G. From II,
K is sitting second to the left of G. From II, 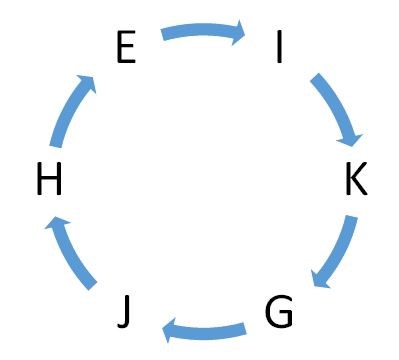 H is sitting second to the left of G.
H is sitting second to the left of G.
____ in reserve requirements ____ the money supply since it causes the money multiplier to ____.
Consider an exchange economy with two agents, 1 and 2, and two goods, X and Y. Each agent's consumption set is in +R2. The endowments of agents 1 and 2 ...
The "Multiplier" effect is larger when the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is:
If coefficient of correlation rxy= 1, then
In a simple linear regression model Y = β0 + β1X + u, the Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) estimator is "best" because it:
What does the Weak Axiom of Revealed Preference (WARP) state?
Suppose the following bilateral spot exchange rates are being quoted for the Danish krone (DKK), the US dollar (US$) and the euro (€):
US$/€ ...
Locus point of Isoquants wherein the marginal productivity of one of the factors is 0 is called
Demand and supply equations were given as Qd = 300 - P, Qs = P/2 and govt imposes specific tax you had to find quantity at which tax revenue is maximized?
Probability that A will be alive in 20 years is 0.7 and probability that B will be alive in 20 years is 0.6, then what is the probability that they bot...
Relevant for Exams:



