Question
A company’s quick ratio is 1.2. If inventory were
purchased for cash, the:Solution
As the quick ratio includes cash but no inventory, there will be a change in the numerator on account of decrease in cash (which is a current asset). Denominator will remain unchanged. So overall, quick ratio will decrease after this change. For example: if quick ratio is 1.2, and if current assets are 1200 and current liabilities are 1000 (1200/1000 =1.2). if we purchase inventory (let’s say for Rs 100), then it will not make a difference in quick assets which exclude inventory. But they include cash, then there will be a reduction in quick assets. Quick assets then will become: 1200 -100 = 1100. There is no change in a liability here. So new quick ratio will become: 1100/1000 = 1.1. So, clearly answer will be (a). There is a reduction in a numerator and result is a lesser quick ratio as compared to the previous one.
Who has written the novel ‘Ajay to Yogi Adityanath’?
Which one of the following is not an iron ore?
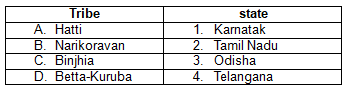
Consider the following pairs:
Which NBFCs are now allowed to co-lend with private lenders under RBI’s 2025 Co-Lending Arrangement reforms?
According to a joint report by India Cellular & Electronics Association (ICEA) and Accenture, what is the estimated revenue potential that circular busi...
Which tribal community celebrates the festival called Sohrai, derived from the paleolithic age word 'soro'?
In which year was Raj Bhavan established in Nainital?
Regarding the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), consider the following statements:
1.The NHRC investigates complaints related to human rig...
India recently won the 2024 ICC T20 World Cup for the second time. In which year did India first win the ICC T20 World Cup?
'Mukhyamantri Ladli Behna Awas Yojana' has been launched in which state?
Relevant for Exams:



