Question
What term is used to describe the population that
results from the sowing of hybrid seeds?Solution
Explanation: When hybrid seeds are sown (often from F1 hybrids), the resulting plants are typically heterozygous at most gene loci because they inherit different alleles from the two parent plants. The plants of the first generation (F1) are genetically uniform in terms of the cross, meaning they are mostly homogeneous with regard to their heterozygous genetic makeup. This population is considered homogeneous in the sense that all plants are hybrid and heterozygous, despite having a mix of genes compared to pure-breeding lines. Over subsequent generations, segregation occurs, leading to genetic diversity (heterogeneous population).
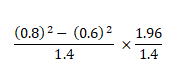
If 3y-3/y=18 then find the value of y² +1/y²
If x2 – 5x + 1 = 0, then find the value of {x2 + (1/x2)}.
If a = 2 + √3, then the value of `(a^(6) + a^(4) + a^(2) + 1)/(a^(3))` is
If √t + (1/√t) = 5, then find the value of t + (1/t).
Given that x8-34x4+1=0, x>0. What is the value of (x3+ x-3)?
If the seven-digit number 94x29y6 is divisible by 72, then what is the value of (2x+3y) for x ≠ y?
If, 3x + 2y = 15, and 2xy = 12, and 3x > 2y, then find the value of 27x³ – 8y³.
If (a + b) = 7 and ab = 10, then find the value of (a 2 + b 2 ).
If x + 1/x = 5 then find out the value of x⁵ + 1/(x⁵)?



